
Navigating Lesser-Known EU Sanctions: A Focus Beyond Asset Freeze
The European Union (EU) has imposed an extensive array of 290 restrictive measures, also known as sanctions, addressing various global issues. While the asset freeze measure stands out as the most well-known, given its frequent mentions and the need to screen against a lengthy list of thousands of sanctioned individuals and entities on EU sanctions lists, this article turns the spotlight onto the less recognized, but equally significant, restrictive measures. EU sanctions impact a wide range of sectors, including insurance, which we will explore in the context of lesser-known measures. Additionally, we will delve into investment-related sanctions and strategies for the insurance industry to comply and mitigate the risk of sanctions violations.
Oct 24
Understanding EU Sanctions: Beyond Asset Freeze
While asset freeze measures have garnered significant attention, there are other vital and less-publicised EU sanctions that require our focus.
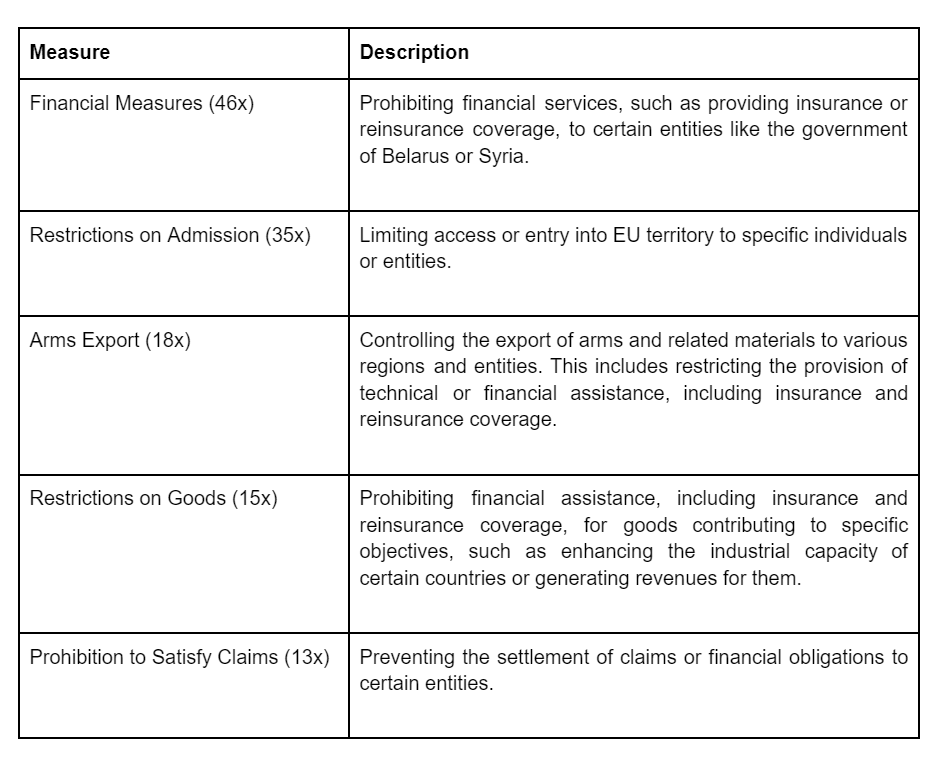
The EU has imposed financial measures, restrictions on admission, arms export controls, restrictions on goods, and prohibitions to satisfy claims on certain entities, such as the governments of Belarus and Syria. These measures are designed to prevent these entities from accessing financial resources, entering EU territory, exporting arms, or importing goods. They also aim to prevent these entities from settling claims or financial obligations.
Here is a table summarizing the measures:
The EU has imposed financial measures, restrictions on admission, arms export controls, restrictions on goods, and prohibitions to satisfy claims on certain entities, such as the governments of Belarus and Syria. These measures are designed to prevent these entities from accessing financial resources, entering EU territory, exporting arms, or importing goods. They also aim to prevent these entities from settling claims or financial obligations.
Here is a table summarizing the measures:
The Risks of Virtual IBANs
While vIBANs offer numerous benefits, they also pose certain risks, particularly in the context of AML/CFT:
Opacity: The "virtual" nature of vIBANs can make it challenging to identify the ultimate beneficiary of a transaction, potentially hindering efforts to trace funds and detect suspicious activity.
Anonymity: vIBANs can be used to mask the identity of the payer or payee, increasing the risk of money laundering and terrorist financing.
Complexity: The multi-layered structure of vIBANs, with payments routed through various intermediaries, can create complexities in transaction monitoring and due diligence processes.
Opacity: The "virtual" nature of vIBANs can make it challenging to identify the ultimate beneficiary of a transaction, potentially hindering efforts to trace funds and detect suspicious activity.
Anonymity: vIBANs can be used to mask the identity of the payer or payee, increasing the risk of money laundering and terrorist financing.
Complexity: The multi-layered structure of vIBANs, with payments routed through various intermediaries, can create complexities in transaction monitoring and due diligence processes.
A New Era of Transparency and Compliance
The good news is that with the implementation of the new Anti-Money Laundering Regulation (AMLR) in 2027, virtual IBANs are finally gaining regulatory recognition. This means increased transparency and clearer guidelines for financial institutions (FIs) leveraging this technology.
The AMLR introduces specific KYC requirements for vIBANs, addressing the concerns around identifying the ultimate beneficiary of transactions. The regulation mandates that FIs must:
The AMLR introduces specific KYC requirements for vIBANs, addressing the concerns around identifying the ultimate beneficiary of transactions. The regulation mandates that FIs must:
- Identify and verify the identity of the individual or legal entity using the vIBAN.
- Identify the associated bank or payment account linked to the vIBAN.
- Ensure that information about the vIBAN user can be obtained quickly from the issuing institution.
Why This Matters
These changes are significant because they will necessitate more robust AML/CFT measures for FIs using vIBANs, including:
- Enhanced due diligence on vIBAN users
- More effective sanctions screening
- Tighter transaction monitoring
Bridging the Gap Until 2027
While the AMLR comes into effect in 2027, regulators are already taking steps to address the risks associated with vIBANs. The BaFin, in its "Risk in Focus 2025" report, highlighted the challenges vIBANs pose to money laundering prevention. Similarly, the Central Bank of Ireland has announced that details of vIBANs will be recorded in national Bank Account Registers to aid law enforcement agencies in tracing funds.
Navigating the vIBAN Landscape
It's crucial for FIs to proactively assess the impact of these upcoming changes and adapt their compliance frameworks accordingly. This includes:
- Reviewing and updating KYC procedures for vIBAN users
- Strengthening transaction monitoring systems
- Ensuring compliance with data sharing requirements
The Future of Virtual IBANs
The AMLR marks a significant step towards greater transparency and accountability in the use of virtual IBANs. By implementing robust KYC and transaction monitoring measures, FIs can harness the benefits of vIBANs while mitigating the associated AML/CFT risks.
Stay Informed
Join us next week for another edition of Compliance Insight, where we'll continue to explore the latest developments in the world of financial crime compliance.

Simon Academy © 2025
Company
-
About
-
Careers
-
Team
-
Contact
